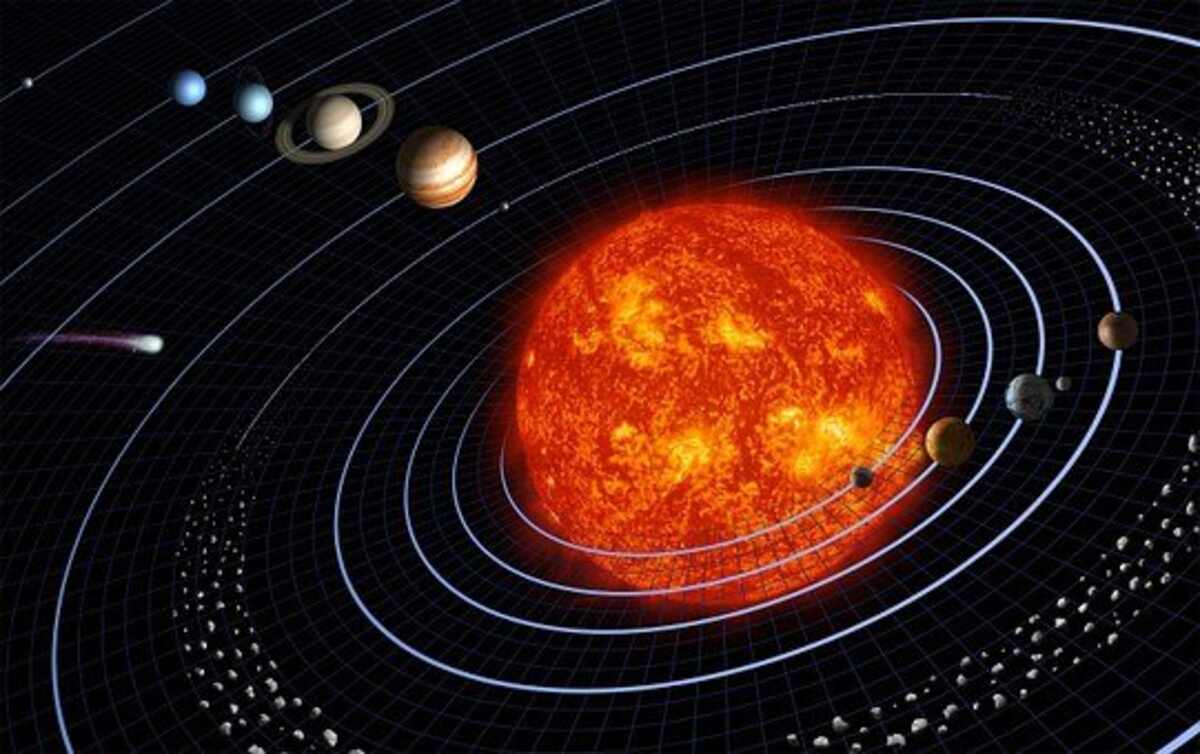
The Solar System is a gravitationally bound system comprised of the Sun and the objects that orbit the Sun. This system formed when a giant interstellar molecular cloud collapsed under the Sun’s gravitational pull. The Sun contains most of the Solar System’s mass, while other objects make up the remaining mass. The other objects in the Solar System include planets, moons, and dwarf planets such as Pluto.
Planets orbit around the Sun
Earth travels in an elliptical orbit around the Sun. The Earth would travel in a straight line if not for the Sun’s gravitational pull. But the gravity of the Sun alters the Earth’s course, causing it to make the curved orbit that it has.
The solar system was formed from a rotating cloud of dust and gas that revolved around a newly-forming star. The material in this cloud formed planets, which began to spin around the Sun. After formation, the planets continued to rotate around the Sun because the gravitational attraction of the Sun kept them in place. Inertia is a fundamental physical law of motion that applies to all objects in space. For example, even our Moon is in orbit around the Earth because of its gravitational pull.
Asteroids orbit the Sun
Asteroids are small rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. They are too small to be called planets and are formed of material left over from the formation of the Solar System. Jupiter may have prevented the formation of planets, which is why asteroids are so minor. Most asteroids have roughly circular orbits, while a few have highly elliptical orbits. They are all less than one percent of the mass of our Moon.
The giant asteroid is Ceres, which is about one-fourth the size of the Moon and orbits the Sun every 4.6 years. Its composition is mainly inorganic, which explains its spherical form. Asteroids are classified as dwarf planets or asteroids, depending on their composition.
Comets orbit the Sun
Comets are objects orbiting the Sun in our solar system. They are relatively small and composed primarily of water and ice. Their motions are strongly affected by the Sun’s and the planet’s gravitational pull. As they approach the Sun, solar radiation causes the ice on their surface to evaporate. The evaporation process releases molecules that flow away from the comet. This action causes the comet to slow down or accelerate.
Comets were first observed by Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer, in 1577. This discovery led to the discovery of periodic comets. Later, Isaac Newton discovered that comets orbit the Sun in oval-shaped orbits. In addition, Chinese astronomers maintained extensive records of comets for centuries, dating back as far as 240 B.C. These records were necessary for the development of cometary science.
Pluto is a dwarf planet.
Pluto was once classified as a planet, but this classification changed in 2006 due to discoveries that made it appear more like a dwarf planet. As a dwarf planet, Pluto shares its orbit with other bodies in the Kuiper belt. This means Pluto has enough mass to be a planet but not enough to clear its neighborhood. Its mass is far less than all other objects in orbit combined.
Pluto was officially labeled a planet in 1930 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The name came from the Roman god of the underworld, Pluto. However, in 2006, the IAU redefined the concept of planets, and Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet. Its small size and limited ability to absorb space rocks make it a dwarf planet. The international scientific community celebrated Pluto Demoted Day on August 24th to honor Pluto’s status.
Pluto’s orbit is elliptical.
Pluto has a slightly different orbit than other planets in our solar system. Planets like Neptune, Earth, and Mars all follow nearly circular orbits around the Sun, but Pluto’s orbit is highly elliptical and varies significantly. For example, it is closer to the Sun during its perihelion period than it is during its aphelion period. As a result, Pluto spends about 20 years of each orbit close to the Sun.
Pluto’s orbit is highly elliptical in the solar system, which means it travels around the Sun at 17 degrees. This makes Pluto’s orbit unique and gives it unique characteristics. At times, it crosses the orbit of Neptune.
Pluto’s moons orbit the Sun.
Pluto’s moons orbit the Sun in an incredibly eccentric manner. Their rotations are highly irregular, and, as a result, their sunrises and sunsets are unpredictable. All planets orbit the Sun and revolve on its axis, but the planets that orbit Pluto have much more angularity. Like the other moons, that tilt makes sunrises and sunsets very unpredictable. However, science has managed to predict the timing of these phenomena to an extent.
Pluto’s four moons are tiny compared to their mother planet. The four moons orbit the planet in a chaotic pattern. Each Moon rotates once per orbit of the planet they orbit. The Earth’s Moon rotates once every 27 days and 8 hours, but Pluto’s four moons rotate at different rates. Nix, the smallest of the moons, rotates backward compared to its sister bodies and is tilted on its side.